优秀的js引擎MathJax – 搞定数据公式LaTeX、MathML、AsciiMath
目录

MathJax
支持数学公式LaTex、MathML、AsciiMath,可编辑,支持浏览器,MathJax是最好的插件。输出格式支持Html、SVG等
MathJax官网:https://www.mathjax.org/
Github:https://github.com/mathjax/MathJax
MathJax支持Wordpress、Drupal等流行软件,也支持Markdown和嵌入到自己的网站系统里。
使用文档:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="ie=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width">
<title>MathJax v3 with TeX input and HTML output</title>
<script src="https://polyfill.io/v3/polyfill.min.js?features=es6"></script>
<script>
MathJax = {
tex: {inlineMath: [['$', '$'], ['\\(', '\\)']]}
};
</script>
<script id="MathJax-script" async src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mathjax@3/es5/tex-chtml.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>MathJax v3 beta: TeX input, HTML output test</h1>
<p>
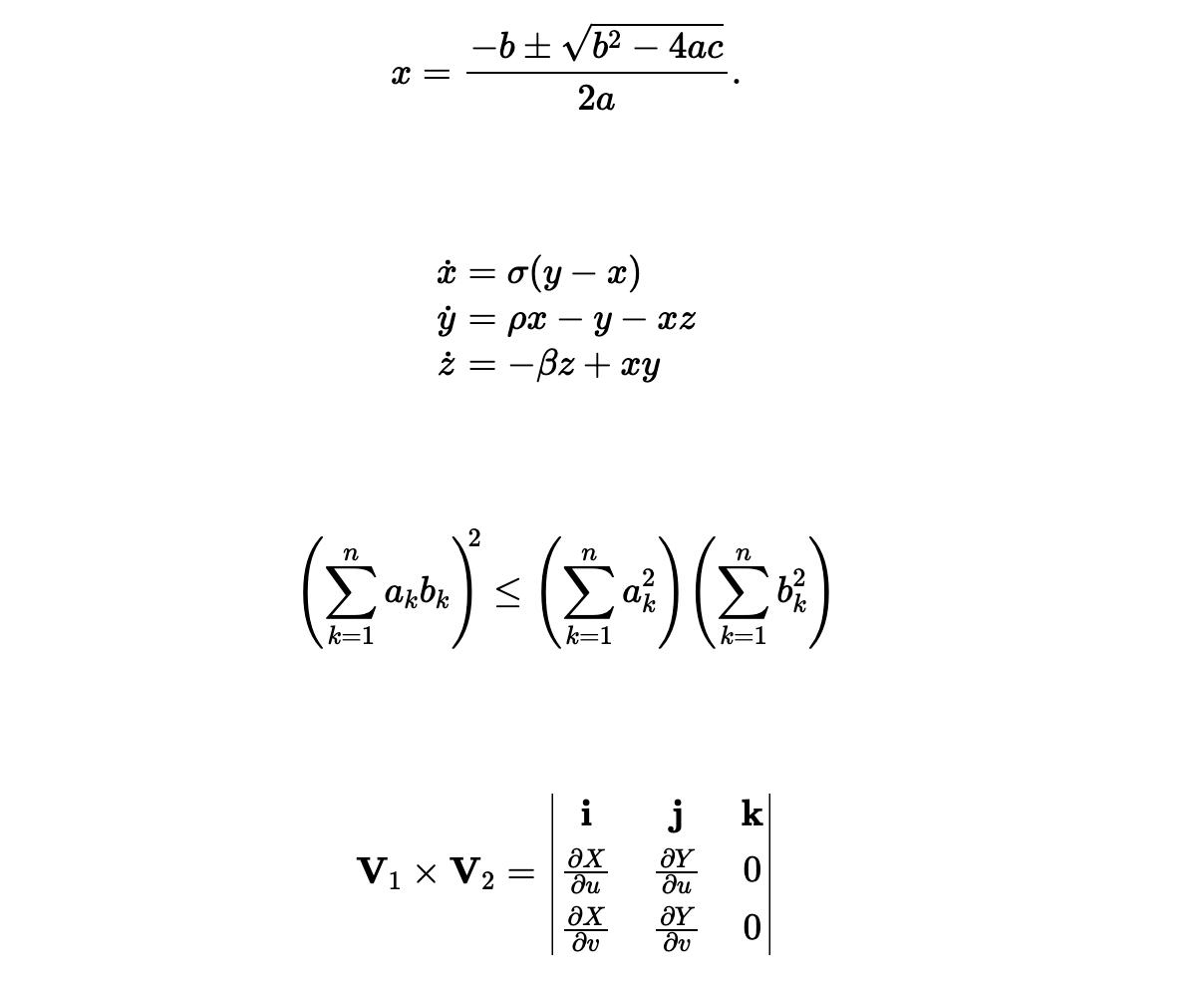
When $a \ne 0$, there are two solutions to \(ax^2 + bx + c = 0\) and they are
$$x = {-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac} \over 2a}.$$
</p>
<h2>The Lorenz Equations</h2>
<p>
\begin{align}
\dot{x} & = \sigma(y-x) \\
\dot{y} & = \rho x - y - xz \\
\dot{z} & = -\beta z + xy
\end{align}
</p>
<h2>The Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality</h2>
<p>\[
\left( \sum_{k=1}^n a_k b_k \right)^{\!\!2} \leq
\left( \sum_{k=1}^n a_k^2 \right) \left( \sum_{k=1}^n b_k^2 \right)
\]</p>
<h2>A Cross Product Formula</h2>
<p>\[
\mathbf{V}_1 \times \mathbf{V}_2 =
\begin{vmatrix}
\mathbf{i} & \mathbf{j} & \mathbf{k} \\
\frac{\partial X}{\partial u} & \frac{\partial Y}{\partial u} & 0 \\
\frac{\partial X}{\partial v} & \frac{\partial Y}{\partial v} & 0 \\
\end{vmatrix}
\]</p>
<h2>The probability of getting \(k\) heads when flipping \(n\) coins is:</h2>
<p>\[P(E) = {n \choose k} p^k (1-p)^{ n-k} \]</p>
<h2>An Identity of Ramanujan</h2>
<p>\[
\frac{1}{(\sqrt{\phi \sqrt{5}}-\phi) e^{\frac25 \pi}} =
1+\frac{e^{-2\pi}} {1+\frac{e^{-4\pi}} {1+\frac{e^{-6\pi}}
{1+\frac{e^{-8\pi}} {1+\ldots} } } }
\]</p>
<h2>A Rogers-Ramanujan Identity</h2>
<p>\[
1 + \frac{q^2}{(1-q)}+\frac{q^6}{(1-q)(1-q^2)}+\cdots =
\prod_{j=0}^{\infty}\frac{1}{(1-q^{5j+2})(1-q^{5j+3})},
\quad\quad \text{for $|q| < 1$}.
\]</p>
<h2>Maxwell's Equations</h2>
<p>
\begin{align}
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{B}} -\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{E}}}{\partial t} & = \frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{\mathbf{j}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{E}} & = 4 \pi \rho \\
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{E}}\, +\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{B}}}{\partial t} & = \vec{\mathbf{0}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{B}} & = 0
\end{align}
</p>
<h2>In-line Mathematics</h2>
<p>Finally, while display equations look good for a page of samples, the
ability to mix math and text in a paragraph is also important. This
expression $\sqrt{3x-1}+(1+x)^2$ is an example of an inline equation. As
you see, MathJax equations can be used this way as well, without unduly
disturbing the spacing between lines.</p>
</body>
</html>
用Mathjax输出的效果如下:
 飞哥专栏
飞哥专栏